QSqlRelationalTableModel¶
- PyQt5.QtSql.QSqlRelationalTableModel
Inherits from QSqlTableModel.
Description¶
The QSqlRelationalTableModel class provides an editable data model for a single database table, with foreign key support.
QSqlRelationalTableModel acts like QSqlTableModel, but allows columns to be set as foreign keys into other database tables.
|
|
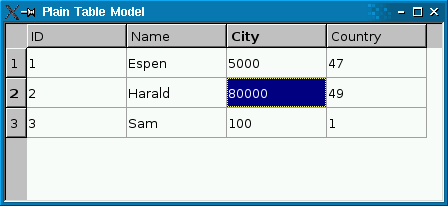
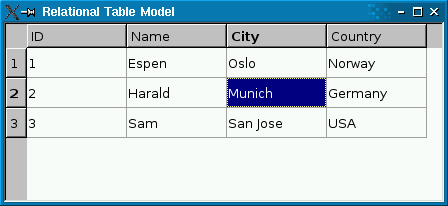
The screenshot on the left shows a plain QSqlTableModel in a QTableView. Foreign keys (city and country) aren’t resolved to human-readable values. The screenshot on the right shows a QSqlRelationalTableModel, with foreign keys resolved into human-readable text strings.
The following code snippet shows how the QSqlRelationalTableModel was set up:
# model->setTable("employee");
# model->setRelation(2, QSqlRelation("city", "id", "name"));
# model->setRelation(3, QSqlRelation("country", "id", "name"));
The setRelation() function calls establish a relationship between two tables. The first call specifies that column 2 in table employee is a foreign key that maps with field id of table city, and that the view should present the city’s name field to the user. The second call does something similar with column 3.
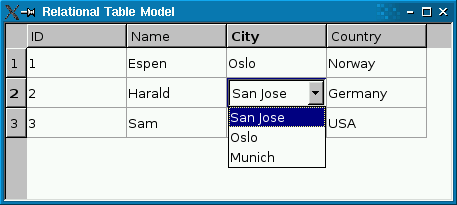
If you use a read-write QSqlRelationalTableModel, you probably want to use QSqlRelationalDelegate on the view. Unlike the default delegate, QSqlRelationalDelegate provides a combobox for fields that are foreign keys into other tables. To use the class, simply call QAbstractItemView::setItemDelegate() on the view with an instance of QSqlRelationalDelegate:
# QTableView *view = new QTableView;
# view->setModel(model);
# view->setItemDelegate(new QSqlRelationalDelegate(view));
The relationaltablemodel example illustrates how to use QSqlRelationalTableModel in conjunction with QSqlRelationalDelegate to provide tables with foreign key support.
Notes:
The table must have a primary key declared.
The table’s primary key may not contain a relation to another table.
If a relational table contains keys that refer to non-existent rows in the referenced table, the rows containing the invalid keys will not be exposed through the model. The user or the database is responsible for keeping referential integrity.
If a relation’s display column name is also used as a column name in the relational table, or if it is used as display column name in more than one relation it will be aliased. The alias is the relation’s table name, display column name and a unique id joined by an underscore (e.g. tablename_columnname_id). fieldName() will return the aliased column name. All occurrences of the duplicate display column name are aliased when duplication is detected, but no aliasing is done to the column names in the main table. The aliasing doesn’t affect QSqlRelation, so QSqlRelation::displayColumn() will return the original display column name.
The reference table name is aliased. The alias is the word “relTblAl” and the relationed column index joined by an underscore (e.g. relTblAl_2). The alias can be used to filter the table (For example, setFilter(“relTblAl_2=’Oslo’ OR relTblAl_3=’USA’”)).
When using setData() the role should always be EditRole, and when using data() the role should always be DisplayRole.
See also
Enums¶
- JoinMode
See also
Member
Value
Description
InnerJoin 0
Inner join mode, return rows when there is at least one match in both tables.
LeftJoin 1
Left join mode, returns all rows from the left table (table_name1), even if there are no matches in the right table (table_name2).
Methods¶
- __init__(parent: QObject = None, db: QSqlDatabase = QSqlDatabase())
Creates an empty QSqlRelationalTableModel and sets the parent to parent and the database connection to db. If db is not valid, the default database connection will be used.
- clear()
TODO
- data(QModelIndex, role: int = Qt.ItemDataRole.DisplayRole) → Any
TODO
- insertRowIntoTable(QSqlRecord) → bool
TODO
- orderByClause() → str
TODO
- relation(int) → QSqlRelation
Returns the relation for the column column, or an invalid relation if no relation is set.
See also
- relationModel(int) → QSqlTableModel
Returns a QSqlTableModel object for accessing the table for which column is a foreign key, or 0 if there is no relation for the given column.
The returned object is owned by the QSqlRelationalTableModel.
See also
- removeColumns(int, int, parent: QModelIndex = QModelIndex()) → bool
TODO
- revertRow(int)
TODO
- select() → bool
TODO
- selectStatement() → str
TODO
- setData(QModelIndex, Any, role: int = Qt.ItemDataRole.EditRole) → bool
TODO
- setJoinMode(JoinMode)
Sets the SQL joinMode to show or hide rows with NULL foreign keys. In InnerJoin mode (the default) these rows will not be shown: use the LeftJoin mode if you want to show them.
See also
- setRelation(int, QSqlRelation)
Lets the specified column be a foreign index specified by relation.
Example:
# model->setTable("employee");# model->setRelation(2, QSqlRelation("city", "id", "name"));The call specifies that column 2 in table
employeeis a foreign key that maps with fieldidof tablecity, and that the view should present thecity’snamefield to the user.Note: The table’s primary key may not contain a relation to another table.
See also
- setTable(str)
TODO
- updateRowInTable(int, QSqlRecord) → bool
TODO