QLineF¶
- PyQt5.QtCore.QLineF
Description¶
The QLineF class provides a two-dimensional vector using floating point precision.
A QLineF describes a finite length line (or line segment) on a two-dimensional surface. QLineF defines the start and end points of the line using floating point accuracy for coordinates. Use the toLine() function to retrieve an integer based copy of this line.
|
|
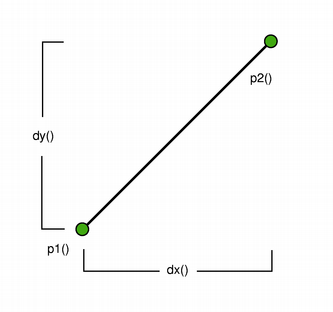
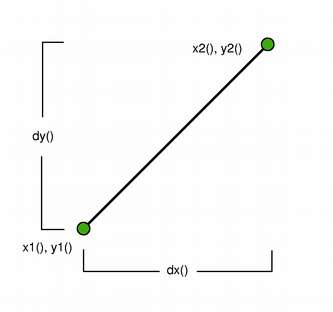
The positions of the line’s start and end points can be retrieved using the p1(), x1(), y1(), p2(), x2(), and y2() functions. The dx() and dy() functions return the horizontal and vertical components of the line, respectively.
The line’s length can be retrieved using the length() function, and altered using the setLength() function. Similarly, angle() and setAngle() are respectively used for retrieving and altering the angle of the line. Use the isNull() function to determine whether the QLineF represents a valid line or a null line.
The intersect() function determines the IntersectType for this line and a given line, while the angleTo() function returns the angle between the lines. In addition, the unitVector() function returns a line that has the same starting point as this line, but with a length of only 1, while the normalVector() function returns a line that is perpendicular to this line with the same starting point and length.
Finally, the line can be translated a given offset using the translate() function, and can be traversed using the pointAt() function.
Enums¶
- IntersectType
Describes the intersection between two lines.

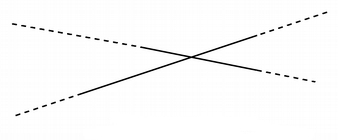
intersect() will also return this value if the intersect point is within the start and end point of only one of the lines.
See also
Member
Value
Description
BoundedIntersection 1
The two lines intersect with each other within the start and end points of each line.
NoIntersection 0
Indicates that the lines do not intersect; i.e. they are parallel.
UnboundedIntersection 2
The two lines intersect, but not within the range defined by their lengths. This will be the case if the lines are not parallel.
Methods¶
- __init__()
TODO
- __init__(QLine)
TODO
- __init__(QLineF)
TODO
- __init__(float, float, float, float)
TODO
- angle() → float
Returns the angle of the line in degrees.
The return value will be in the range of values from 0.0 up to but not including 360.0. The angles are measured counter-clockwise from a point on the x-axis to the right of the origin (x > 0).
See also
- angleTo(QLineF) → float
TODO
- __bool__() → int
TODO
- center() → QPointF
TODO
- dx() → float
TODO
- dy() → float
TODO
- __eq__(QLineF) → bool
TODO
-
@staticmethod
fromPolar(float, float) → QLineF Returns a QLineF with the given length and angle.
The first point of the line will be on the origin.
Positive values for the angles mean counter-clockwise while negative values mean the clockwise direction. Zero degrees is at the 3 o’clock position.
- intersect(QLineF, Union[QPointF, QPoint]) → IntersectType
TODO
- intersects(QLineF) → (IntersectType, QPointF)
TODO
- isNull() → bool
TODO
- length() → float
Returns the length of the line.
See also
- __ne__(QLineF) → bool
TODO
- normalVector() → QLineF
TODO
- pointAt(float) → QPointF
TODO
- __repr__() → str
TODO
- setAngle(float)
Sets the angle of the line to the given angle (in degrees). This will change the position of the second point of the line such that the line has the given angle.
Positive values for the angles mean counter-clockwise while negative values mean the clockwise direction. Zero degrees is at the 3 o’clock position.
See also
- setLength(float)
See also
- setLine(float, float, float, float)
TODO
- toLine() → QLine
TODO
- translate(float, float)
TODO
- translated(float, float) → QLineF
TODO
- unitVector() → QLineF
Returns the unit vector for this line, i.e a line starting at the same point as this line with a length of 1.0.
See also
- x1() → float
TODO
- x2() → float
TODO
- y1() → float
TODO
- y2() → float
TODO