QLine露
- PyQt5.QtCore.QLine
Description露
The QLine class provides a two-dimensional vector using integer precision.
A QLine describes a finite length line (or a line segment) on a two-dimensional surface. The start and end points of the line are specified using integer point accuracy for coordinates. Use the QLineF constructor to retrieve a floating point copy.
|
|
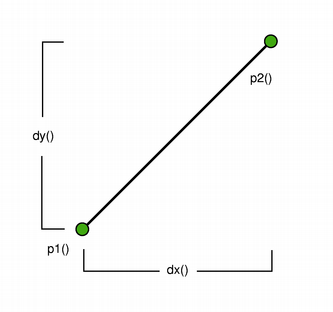
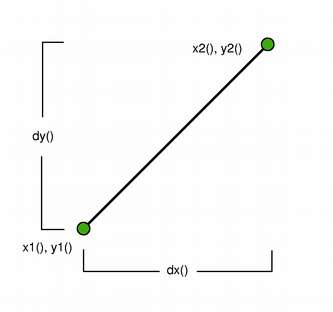
The positions of the line鈥檚 start and end points can be retrieved using the p1(), x1(), y1(), p2(), x2(), and y2() functions. The dx() and dy() functions return the horizontal and vertical components of the line. Use isNull() to determine whether the QLine represents a valid line or a null line.
Finally, the line can be translated a given offset using the translate() function.
Methods露
- __init__()
TODO
- __init__(QLine)
TODO
- __init__(int, int, int, int)
TODO
- __bool__() → int
TODO
- center() → QPoint
TODO
- dx() → int
TODO
- dy() → int
TODO
- __eq__(QLine) → bool
TODO
- isNull() → bool
TODO
- __ne__(QLine) → bool
TODO
- __repr__() → str
TODO
- setLine(int, int, int, int)
TODO
- translate(QPoint)
TODO
- translate(int, int)
TODO
- translated(int, int) → QLine
TODO
- x1() → int
TODO
- x2() → int
TODO
- y1() → int
TODO
- y2() → int
TODO